
Four Key Benefits and Risks of IOT in Healthcare
Since the Internet of Things (IOT) emerged in the healthcare industry, it’s revealed a number of priceless solutions. It’s helped lower costs, improve efficiency, and given physicians and nurses valuable insights that help guide treatments and reduce common medical errors.
However, as IOT continues to revolutionize healthcare, some major flaws are rearing their heads. IOT can provide incredible benefits to physicians, nurses, and physician assistants, but it can also expose everyone involved to new risks.
As your organization continues or begins implementing and taking advantage of the solutions IOT offers to healthcare, it’s important to have a keen understanding of both the benefits and the risks IOT brings. Let’s take a closer look at some of those factors, starting with the benefits of IOT in healthcare.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices have become increasingly common for use by consumers and healthcare professionals. While products like Fitbits or the Apple Watch are capable of tracking users’ heart rate and other metrics, and other highly-specialized healthcare products allow for monitoring of complex metrics throughout a patient’s daily life.
IOT wearables that monitor metrics like electrocardiograms and blood pressure allow physicians and nurses to understand their patient’s health over the span of a month, rather than a mere 30 minute window during a visit.
Remote Monitoring
One of the most beneficial and widely-applicable benefits of IOT in healthcare is the possibilities for remote monitoring. Remote monitoring allows physicians and nurses to streamline the patient-monitoring process, both in hospitals and while patients are at home. Remote monitoring can be used for things like:
- Glucose Monitoring: Remote glucose monitoring allows physicians to get a more holistic view of their patients’ glucose levels. This offers vastly more accurate results than traditional glucose monitoring, which is essential for determining the best care plan for diabetic patients.
- Heart-Rate Monitoring: Conventional heart-rate monitors must choose either accuracy over time, or patient mobility. With IOT devices, there is no settling: patient heart rates can be monitored accurately, remotely, and regularly.
- Other Kinds of Remote Monitoring: Other conditions like Parkinson’s disease and depression have been exceedingly difficult for physicians and nurses to monitor in the past. Patients could only be monitored for a brief period, resulting in clinicians only getting a snapshot of the patient’s health. Remote monitoring with wearable devices for conditions like these allows clinicians to save time and develop more accurate treatment plans.
Ingestible Sensors
A more radical version of wearable IOT devices is ingestible sensors, or ‘intelligent pills.’ These sensors typically work by relaying information from the ‘pill’ to a wearable patch, which records and collects data.
While the use and application of ingestible sensors is still nascent and less widely adopted compared to wearables, it could prove to be a massive leap forward in diagnostic accuracy. These devices could significantly reduce the need for invasive procedures, and mitigate costly misdiagnoses.
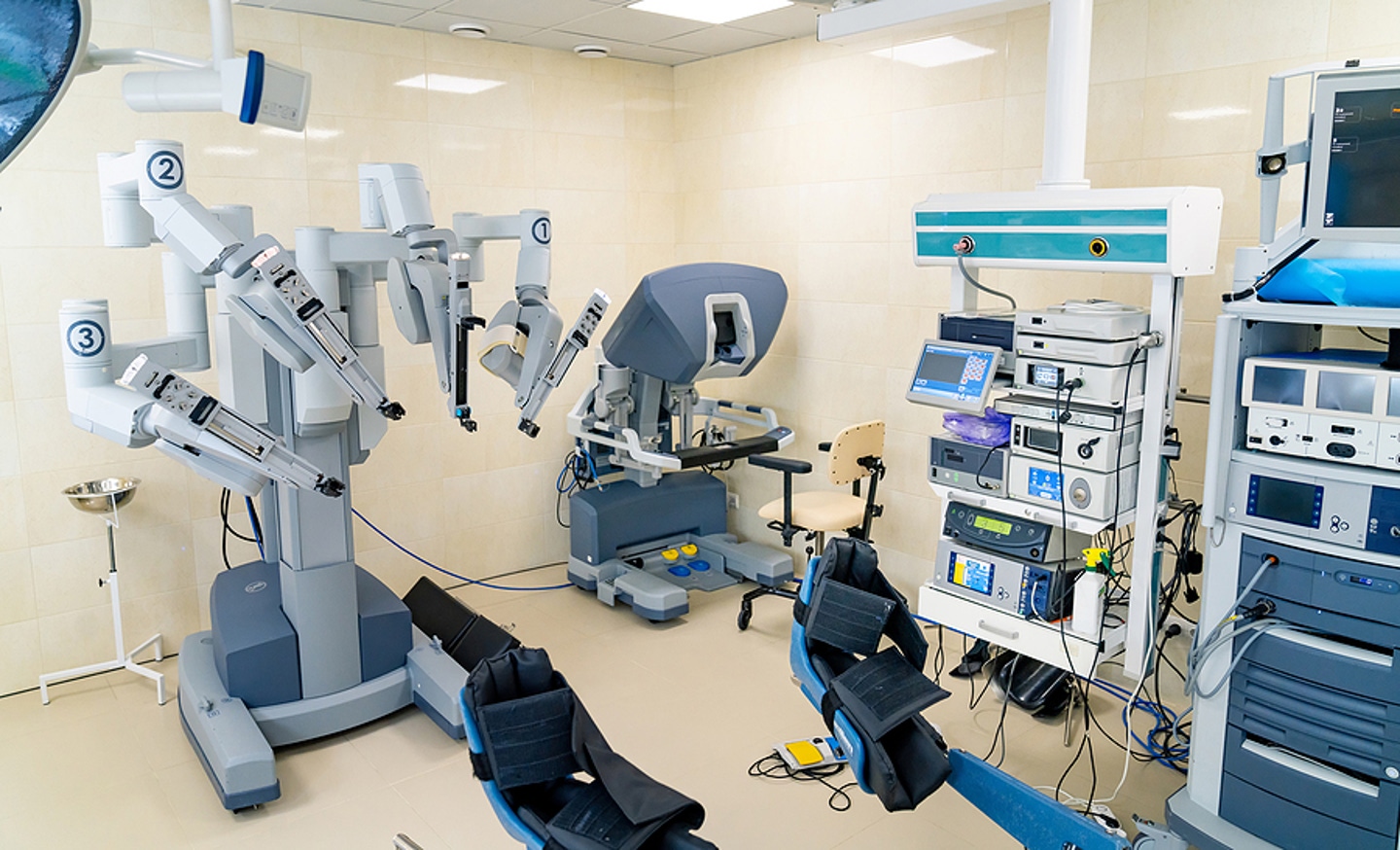
Robotic Surgery
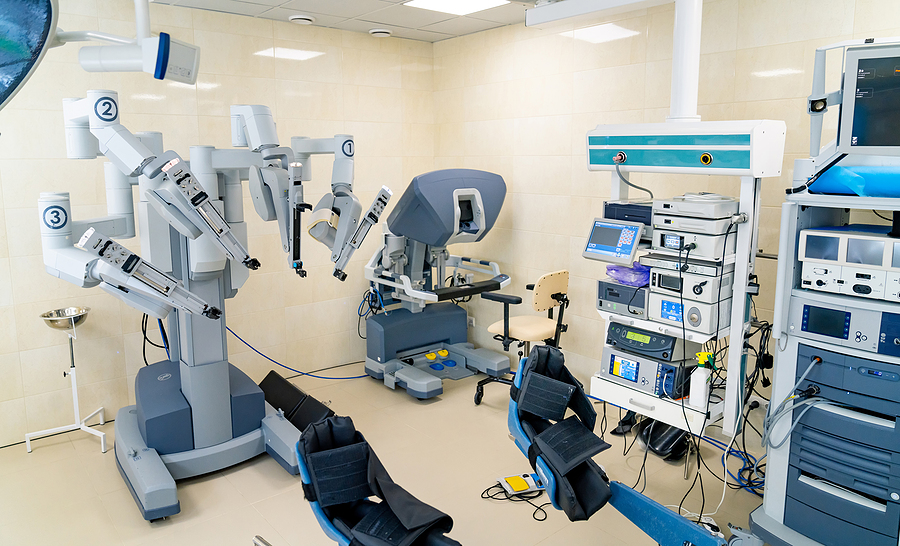

Robot-assisted surgery is an increasingly popular IOT use in healthcare. Robotic surgery could allow surgeons to maximize precision, minimize bleeding, and reduce how invasive a procedure is. Additionally, patients who undergo robot-assisted surgery may have faster recovery times.
With the advent of 5G networks, patients could potentially be operated on by a robot controlled by a specialist thousands of miles away. Not only could robotic surgery improve patient outcomes, it also has the potential to increase access to specialists.
Risks of IOT in Healthcare
IOT in healthcare will be revolutionary, but it won’t come without significant struggles. Currently, there are a number of risks associated with IOT in healthcare. Addressing these is critical for physicians, nurses, physician assistants, and all healthcare specialists to remain compliant.
Problems with IOT Data
One of the largest issues with IOT in healthcare is the data it creates. Wearable devices that track a user’s location in addition to their health information before transmitting that information are vulnerable to be attacked and exploited, risking a patient’s privacy. Additionally, there is a debate over who owns the data that is produced and transmitted by IOT devices such as wearables.
HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA compliance runs hand in hand with the problems IOT in healthcare faces with data. As each device is connected to several networks, the vulnerabilities each device is exposed to are multiplied. Each network a device is connected to should be HIPAA compliant and secured, but this can easily be missed.
Additionally, physicians, nurses, and other health professionals need to be aware of what private health information (PHI) is being collected by an IOT device. Otherwise, they could be violating privacy regulations.
Software or Hardware Malfunctions
Anybody who has used a smartphone or computer can testify to the fact that systems using and transferring information through complex software and hardware can fail. The same holds true for wearables, surgical robots, and ingestible sensors. However, when it comes to IOT in healthcare, the stakes are much higher.
Legacy equipment that fails, software that carries a bug, or systems that aren’t adequately protected against malware or other attacks all pose a serious threat to healthcare organizations. Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks could prevent nurses, physicians, physician assistants from accessing crucial information when they need it most.
Injuries
The most obvious, immediate risks of IOT devices are injuries to patients. Heart-rate monitoring devices that fail to notify a nurse or physician at the proper time could lead to serious injuries and health complications.
Additionally, while wearables can undoubtedly improve the accuracy of information available to physicians, patients could be exposed to additional WiFi signals which may cause injuries.
Stay Up to Date With Medical Advances with CME
The world of healthcare changes quickly, and staying up to date is critical for providing the best patient care possible. A great way to stay up to date is by attending the leading CME conferences.
Continuing medical education conferences expose physicians, nurses, and physician assistants to the latest advancements in care, best practices, and strategies for mitigating risk throughout their healthcare organizations.
Continuing Education Company has been a leader in the CME industry for over 30 years. Our conferences feature great, engaging speakers, experts from a variety of fields, and are held in jaw-dropping locations across the U.S. To learn more about CEC’s upcoming conferences, check out our calendar today!